The Simplified Molecular Input Line Entry specification or SMILES is a specification for unambiguously describing the structure of chemical molecules using short ASCII strings.
In July 2006, the IUPAC introduced the InChI as a standard for formula representation. SMILES is generally considered to have the advantage of being slightly more human-readable than InChI; it also has a wide base of software support with extensive theoretical (e.g., graph theory) backing.
SMILES strings can be imported by most molecule editors for conversion back into two-dimensional drawings or three-dimensional models of the molecules.
SMILES uses atomic symbols and a set of intuitive rules and uses hydrogen-suppressed molecular graphs (HSMG).
Canonical SMILES and Isomeric SMILES
The term Canonical SMILES refers to the version of the SMILES specification that includes rules for ensuring that each distinct chemical molecule has a single unique SMILES representation
• A common application of Canonical SMILES is for indexing and ensuring uniqueness of molecules in a database.
The term Isomeric SMILES refers to the version of the SMILES specification that includes extensions to support the specification of isotopes, chirality, and configuration about double bonds
• A notable feature of these rules is that they allow rigorous partial specification of chirality.
Symbols Application in SMILES
1. Atoms
- Atoms are represented by the standard abbreviation of the chemical elements, in square brackets, such as [Au] for gold. Brackets can be omitted for the "organic subset" of B, C, N, O, P, S, F, Cl, Br, and I. All other elements must be enclosed in brackets. If the brackets are omitted, the proper number of implicit hydrogen atoms is assumed; for instance the SMILES for water is simply O.
- An atom holding one or more electrical charges is enclosed in brackets, followed by the symbol H if it is bonded to one or more atoms of hydrogen, followed by the number of hydrogen atoms then by the sign '+' for a positive charge or by '-' for a negative charge. The number of charges is specified after the sign (except if there is one only).
- Bonds between aliphatic atoms are assumed to be single unless specified otherwise and are implied by adjacency in the SMILES string. For example the SMILES for ethanol can be written as CCO. Ring closure labels are used to indicate connectivity between non-adjacent atoms in the SMILES string.
- Bonds symbols in SMILES :
- SINGLE* -
- DOUBLE =
- TRIPLE #
- AROMATIC :
* can be omitted
- SINGLE* -
- DOUBLE =
- TRIPLE #
- AROMATIC :
3. Aromaticity
- Aromatic C, O, S and N atoms are shown in their lower case 'c', 'o', 's' and 'n' respectively. Benzene, pyridine and furan can be represented respectively by the SMILES c1ccccc1, n1ccccc1 and o1cccc1. Bonds between aromatic atoms are, by default, aromatic although these can be specified explicitly using the ':' symbol.
- Isomeric configuration indicated by forward "/" and backward "\" slashes.
- Chirality is indicated by the "@" symbol.
Examples of Application on Some Molecules
| Molecule | Structure | SMILES Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Dinitrogen | N≡N | N#N |
| Methyl isocyanate (MIC) | CH3–N=C=O | CN=C=O |
| Copper(II) sulfate | Cu2+ SO42- | [Cu+2].[O-]S(=O)(=O)[O-] |
| Oenanthotoxin (C17H22O2) |  | CCC[C@@H](O)CC\C=C\C=C\C#CC#C\C=C\CO |
| Pyrethrin II (C22H28O5) |  | COC(=O)C(\C)=C\C1C(C)(C)[C@H]1C(=O)O[C@@H]2C(C)=C(C(=O)C2)CC=CC=C |
| Aflatoxin B1 (C17H12O6) |  | O1C=C[C@H]([C@H]1O2)c3c2cc(OC)c4c3OC(=O)C5=C4CCC(=O)5 |
| Glucose (glucopyranose) (C6H12O6) |  | OC[C@@H](O1)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)1 |
| Bergenin (cuscutin) (a resin) (C14H16O9) |  | OC[C@@H](O1)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]2[C@@H]1c3c(O)c(OC)c(O)cc3C(=O)O2 |
| A pheromone of the Californian scale insect |  | CC(=O)OCCC(/C)=C\C[C@H](C(C)=C)CCC=C |
| 2S,5R-Chalcogran: a pheromone of the bark beetle Pityogenes chalcographus [2] | ![(2S,5R)-2-ethyl-1,6-dioxaspiro[4.4]nonane](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/8e/2S%2C5R-chalcogran-skeletal.svg/195px-2S%2C5R-chalcogran-skeletal.svg.png) | CC[C@H](O1)CC[C@@]12CCCO2 |
| Vanillin |  | O=Cc1ccc(O)c(OC)c1 |
| Melatonin (C13H16N2O2) |  | CC(=O)NCCC1=CNc2c1cc(OC)cc2 |
| Flavopereirin (C17H15N2) |  | CCc(c1)ccc2[n+]1ccc3c2Nc4c3cccc4 |
| Nicotine (C10H14N2) | 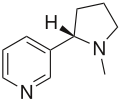 | CN1CCC[C@H]1c2cccnc2 |
| Alpha-thujone (C10H16O) |  | CC(C)[C@@]12C[C@@H]1[C@@H](C)C(=O)C2 |
| Thiamin (C12H17N4OS+) (vitamin B1) |  | OCCc1c(C)[n+](=cs1)Cc2cnc(C)nc(N)2 |
SMILESCAS Database
No comments:
Post a Comment